Jump to:
Looking for a garden greenhouse? You will find many options on the market which list polycarbonate as one of their materials. But what is the difference between polycarbonate and a traditional glass greenhouse? And which is better? Let’s
What is a Polycarbonate Greenhouse?
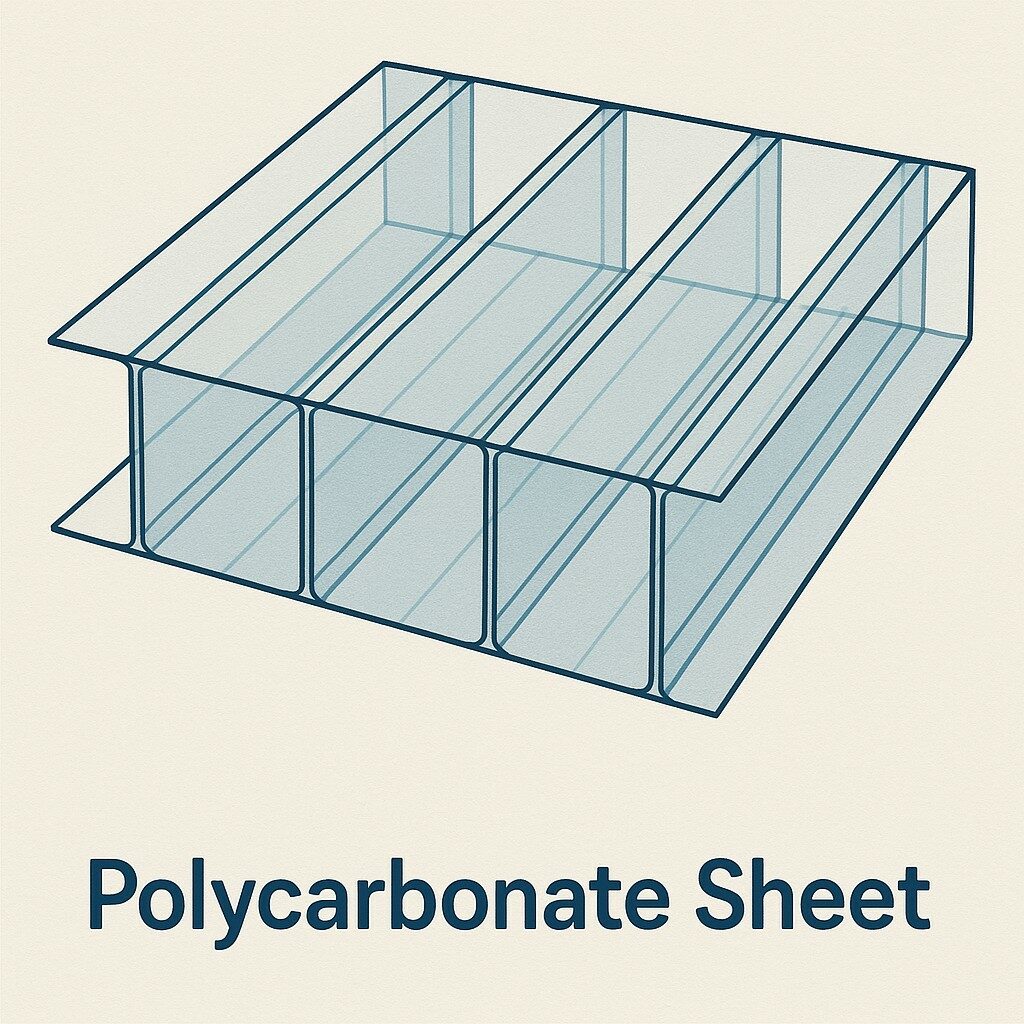
Polycarbonate greenhouses have windows made of translucent plastic sheets instead of glass. These sheets consist of two panes, joined by lots of internal ribs that create small hollow air pockets.
Here is a cross section of what this looks like, up close:
Advantages of Glass Greenhouses
Glass greenhouses can look better
Ordinary glass provides a clear view of your plants and a shiny appearance. If you are growing attractive plants and want visitors to be able to see them.
However, this benefit is also available with a clear wall greenhouse, which uses transparent styrene glazing on 4 sides.

It might surprise you to learn that this is the extent of the advantages that glass has over polycarbonate. Glass is more expensive, breaks more easily, and doesn’t help your plants as much. Keep reading to find out more.
Advantages of Polycarbonate Greenhouses
Polycarbonate glazing holds in heat for longer

Garden greenhouses trap the heat from the sun within the room and allow for the growing season. Without heat, they’re pretty much useless. Although glass is quick to heat up and cool down, it doesn’t hold heat for long. As a result, this can be fatal for plants, such as tropical plants, during the colder months.
Polycarbonate panels always beat glass on insulation. Most are made of double-walled material – with two sheets of film put together with space between them. This internal buffer space makes them a much better heat retainer and insulator.
Polycarbonate material is also more cost-effective. Alongside heat, it’s also a great noise insulator. So, if you’re looking for a quiet environment while you are gardening, polycarbonate is the way to go!
Polycarbonate is more durable and safer than glass
Polycarbonate is nearly unbreakable, even in severe weather conditions. Its ability to withstand strong forces while being lightweight contributes to its longevity. This provides clear safety benefits over glass.
This material can endure more pressure before breaking compared to glass. Drop a polycarbonate panel, and it’s less likely to shatter. Even if a football hits the window, the chances of damage are minimal, unlike with glass.

Strong polycarbonate glazing can reduce the risk in everyday use. Accidents happen; having a structure with hard plastic roofing and walls is crucial. Weather conditions and elements like hail and wind can easily damage glass.
Luckily, polycarbonate greenhouses withstand the most stringent tests. Corrugated polycarbonate panels, for instance, are virtually indestructible.
Polycarbonate need less maintenance than glass
Polycarbonate sheets need little to no maintenance, unlike glass, which is a different story. Upkeep is still necessary, but not as often. As polycarbonate panels stay cleaner for longer, they easily achieve that classic greenhouse look.
A shading system is a must for glass structures to protect plants from harsh UV rays. You’ll also need to be more diligent about venting and airflow in case it gets too hot inside.
Better light diffusion and UV protection
Plastic overall is far thicker than glass, resulting in better light diffusion. This means more natural light will spread through, especially with polycarbonate windows. This gives your beautiful plants all the sun exposure they need.
Polycarbonate also better protects plants against certain harmful types of UV sun radiation. All thanks to its natural ultraviolet filter properties.
Polycarbonate sheets are easier to install

Glass is a bit more fragile and heavier than polycarbonate. Due to their size and weight, handling larger glass panes may be difficult. Most glass greenhouses also require professional assembly, which often takes much longer.
Polycarbonate, in contrast, can be installed in bigger sections and is more lightweight. When doing so, extra care is essential, though, to prevent damage to the sheet, especially the edges. It also needs to be sealed well along any edge that has been cut. Otherwise, moisture, mould, and bugs can get into the void.
With a polycarbonate unit, the installation could be done easily by yourself and a friend. This will save you the extra cost of hiring a builder or installation fees.
Customisable Polycarbonate Greenhouses
Glass greenhouses generally have a metal frame. Meanwhile, the wooden frames on polycarbonate structures welcome painting possibilities. You can paint and customise them and breathe more life into your unit. This is such a wonderful perk if you’re a green thumb fond of art!
Polycarbonate greenhouses are cheaper than glass
The cost for both polycarbonate and glass designs can vary depending on the source and quality of the material. Sure, you can save a good deal of money by building your own greenhouse from reclaimed glass panels. Yet, this can be difficult and requires expertise.
Polycarbonate units are much cheaper, and there are plenty of options. Invest in a quality product from a reliable store to guarantee a longer lifespan. Look no further than Garden Buildings Direct for all your greenhouse needs!
Polycarbonate greenhouses extend the growing season
Polycarbonate is ideal for cultivating fresh vegetables year-round. Thanks to its excellent light transmission distribution. This provides support for the growth of bulb plants, enabling longer cultivation periods. Plus, you’ll save both time and money on heating costs. This is a big advantage over traditional horticultural glass greenhouses.
See more on how to grow bulb plants.
Round-up
Both polycarbonate and glass can make functional greenhouses. However, polycarbonate is often the better choice for novice growers. It provides optimal lighting and heat retention, making it easier to cultivate plants. Despite being slightly more expensive up front, such options are low-maintenance, too. This allows gardeners to focus on their plants rather than ongoing upkeep.
If you’re unsure what to nurture, check out our guide on ‘5 Best Plants To Grow In Your Greenhouse’. For more options, make sure to browse our range of greenhouses for sale.
If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us at 01909 768840.
FAQs
Which is better for a greenhouse: polycarbonate or glass?
Polycarbonate is better. It’s also suitable for gardeners at any level, but especially for beginners. And although glass is great, the benefits of polycarbonate far outweigh its perks.
What’s the lifespan of polycarbonate glazing?
Polycarbonate is a highly durable glazing material often used in greenhouses and roofing. Most high-quality sheets are manufactured with a UV-resistant coating that helps prevent yellowing and degradation from sun exposure. With proper installation and care, UV-protected polycarbonate glazing can last 10 to 15 years or more.
How thick is polycarbonate glazing?
Like glass, the popular thicknesses range between 3 and 6mm.
Are polycarbonate roofs noisy?
Unfortunately, they’re not known for their soundproofing qualities. But an effective solution is to increase the thickness of the sheet to 35-60mm.
Do greenhouses need planning permission?
In most cases, greenhouses fall under permitted development and don't need planning permission. However, you may need it if the structure takes up more than half your garden, exceeds height limits, or is built in front of your house’s main elevation. Rules may be stricter in conservation areas or on listed properties. Always check with your local planning authority to be sure.










